Types Of Solar System
Types of Solar Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
As solar energy continues to gain popularity as a renewable and sustainable energy source, it’s important to understand the different types of solar systems available. Each type serves different needs, whether for residential, commercial, or industrial applications. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of solar systems:
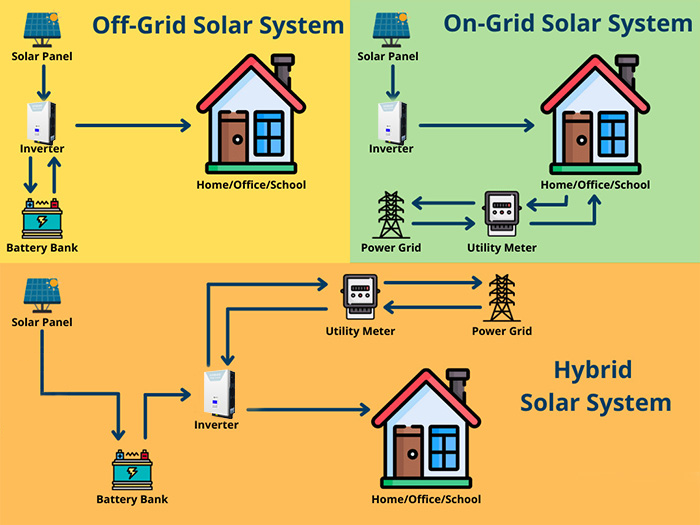
1. Grid-Tied Solar System
A grid-tied solar system, also known as a grid-connected system, is the most common setup for residential and commercial properties. This system is connected to the local electricity grid and operates in sync with it.
Features:
- Solar panels generate power during the day.
- Excess energy is sent back to the grid, which may result in credits or compensation from the utility company (net metering).
- Energy backup is not available during a power outage unless you have a battery storage system.
Best for: Homeowners and businesses looking to reduce their electricity bills with the option to rely on grid power when needed.
2. Off-Grid Solar System
An off-grid solar system operates independently from the electricity grid, providing a self-sufficient power solution. It is ideal for remote areas where the grid connection is unavailable or too expensive.
Features:
- Solar panels generate electricity, which is stored in batteries for use when the sun isn’t shining.
- No need for a connection to the local power grid.
- Requires larger battery storage to ensure a reliable power supply.
Best for: Rural areas, cabins, or remote locations where grid power is not feasible.
3. Hybrid Solar System
A hybrid solar system combines the best of both grid-tied and off-grid systems. It is connected to the grid but also incorporates a battery storage solution.
Features:
- Solar panels generate power, excess energy is stored in batteries.
- Can draw power from the grid when necessary, providing backup during cloudy days or power outages.
- Can be programmed to prioritize using solar or stored energy first, and then draw from the grid.
Best for: Homeowners or businesses looking for energy independence with backup power options.
4. Solar Water Heating System
A solar water heating system uses solar energy to heat water, providing an eco-friendly solution for hot water needs. This type of system consists of solar collectors and a water storage tank.
Features:
- Solar collectors absorb sunlight to heat water.
- A storage tank holds the heated water for later use.
- Can reduce water heating costs significantly.
Best for: Homes or businesses that use a lot of hot water, such as swimming pools, hotels, or residential buildings.
5. Solar Pool Heating System
Similar to solar water heating, solar pool heating systems are designed specifically to keep pool water warm. It uses solar collectors to absorb sunlight and transfer the heat to the pool water.
Features:
- Provides a cost-effective way to extend the swimming season.
- Can be used in conjunction with an existing pool heating system.
- Solar collectors are typically mounted on the roof or a nearby structure.
Best for: Pool owners looking to reduce heating costs and use renewable energy.
6. Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems are mainly used in large-scale energy generation plants rather than residential applications. They use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, usually a receiver, to generate heat, which is then converted into electricity.
Features:
- Uses mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight.
- Typically used for large-scale solar power plants.
- Requires large areas of land.
Best for: Utility-scale energy generation.
Conclusion
The type of solar system you choose depends on your energy needs, location, and whether you want to be connected to the grid or independent. Whether you are looking to reduce your electricity bills, gain energy independence, or contribute to a sustainable future, there’s a solar solution to fit your needs.
